Gravity Die Casting (Permanent Mould Casting) employs the use of steel moulds which allow Aluminum to solidify by gravity. Molten metal filling is ensured by feeder design, while use of fibre glass filters prevent inclusion and oxides from flowing along with the molten Aluminum. The steel moulds will ensure rapid chilling, while ceramic riser cup will ensure proper feeding of molten Aluminum during solidification, resulting in production of very sound quality castings. These castings are heat treatable and provides excellent mechanical properties.Gravity Die Casting (Permanent Mould Casting) employs the use of steel moulds which allow Aluminum to solidify by gravity. Molten metal filling is ensured by feeder design, while use of fibre glass filters prevent inclusion and oxides from flowing along with the molten Aluminum. The steel moulds will ensure rapid chilling, while ceramic riser cup will ensure proper feeding of molten Aluminum during solidification, resulting in production of very sound quality castings. These castings are heat treatable and provides excellent mechanical properties.
Gravity die casting, also known as permanent mold casting, is a metal casting process that involves pouring molten metal into a reusable metal mold or die under the force of gravity. This process is commonly used for producing high-quality, dimensionally accurate metal parts with good surface finish.
Gravity die casting is a versatile manufacturing process suitable for producing a wide range of metal components used in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Here's how the gravity die casting process typically works:
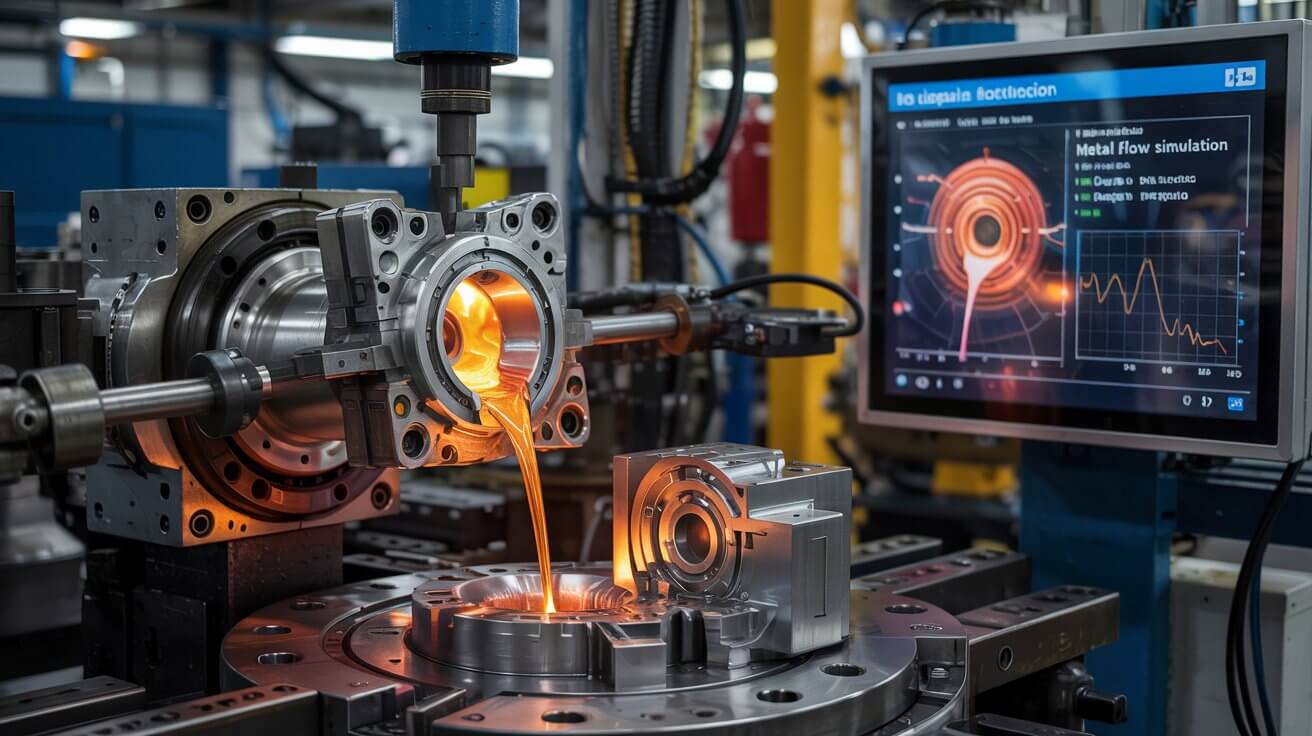

Simulates the casting process in advance, eliminating multiple trials and achieving high quality at the first time.
Read More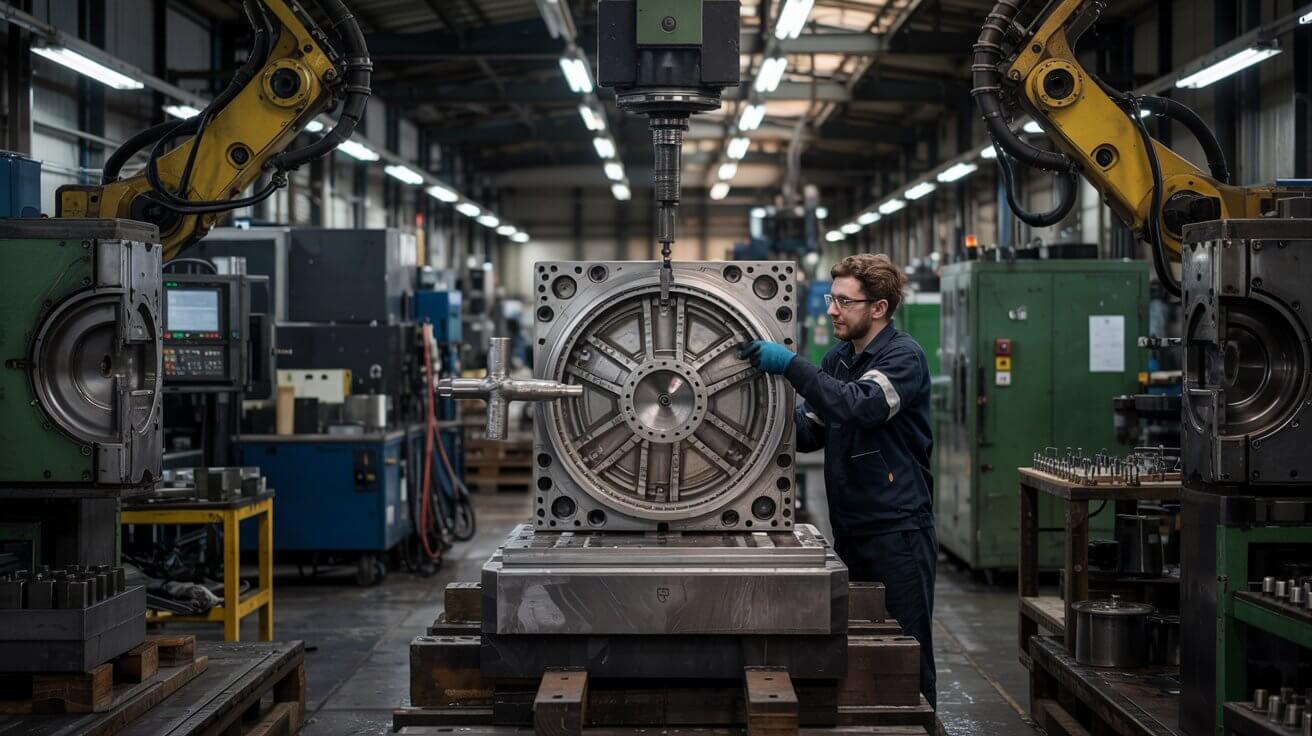
The process begins with the preparation of the mold. The mold, usually made of steel or cast iron, is designed to have the desired shape of the final product. It consists of two halves, the stationary half (the "die") and the movable half (the "core"), which are often machined to high precision.
Read More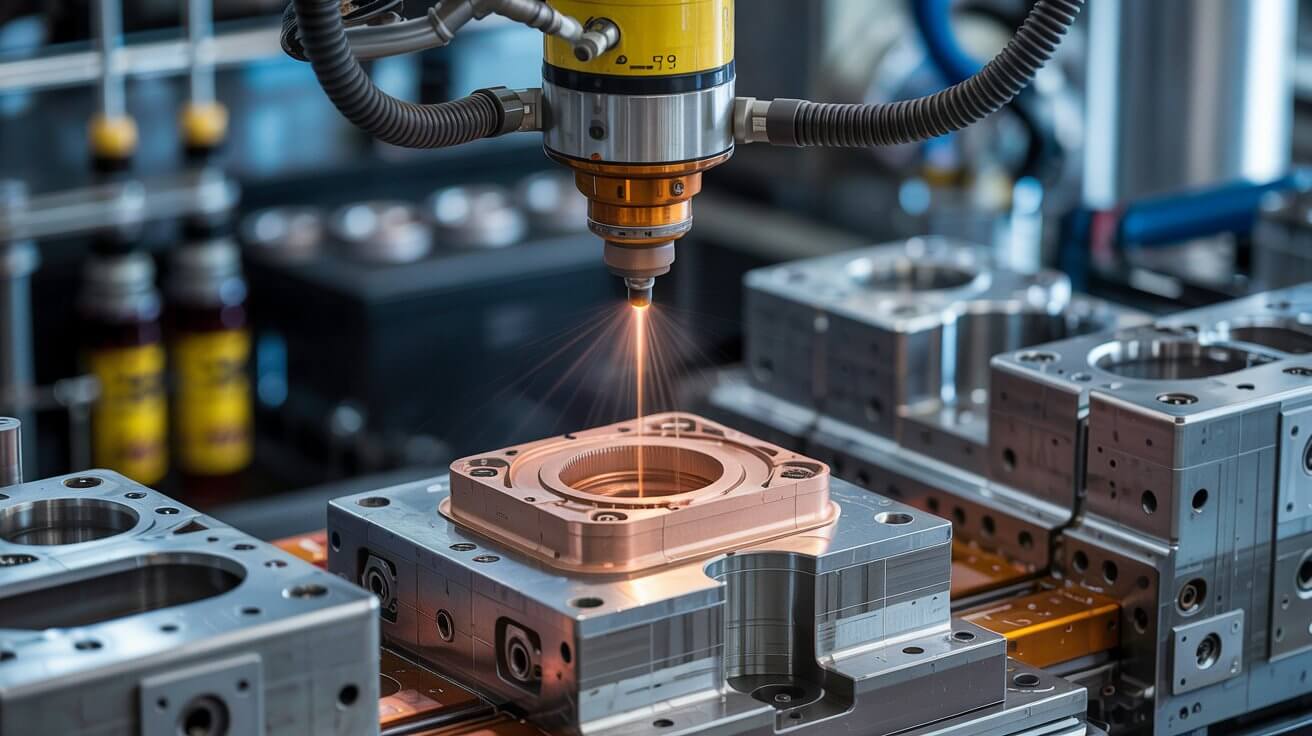
The mold surfaces are coated with a release agent to prevent sticking of the molten metal and aid in the removal of the solidified casting.
Read More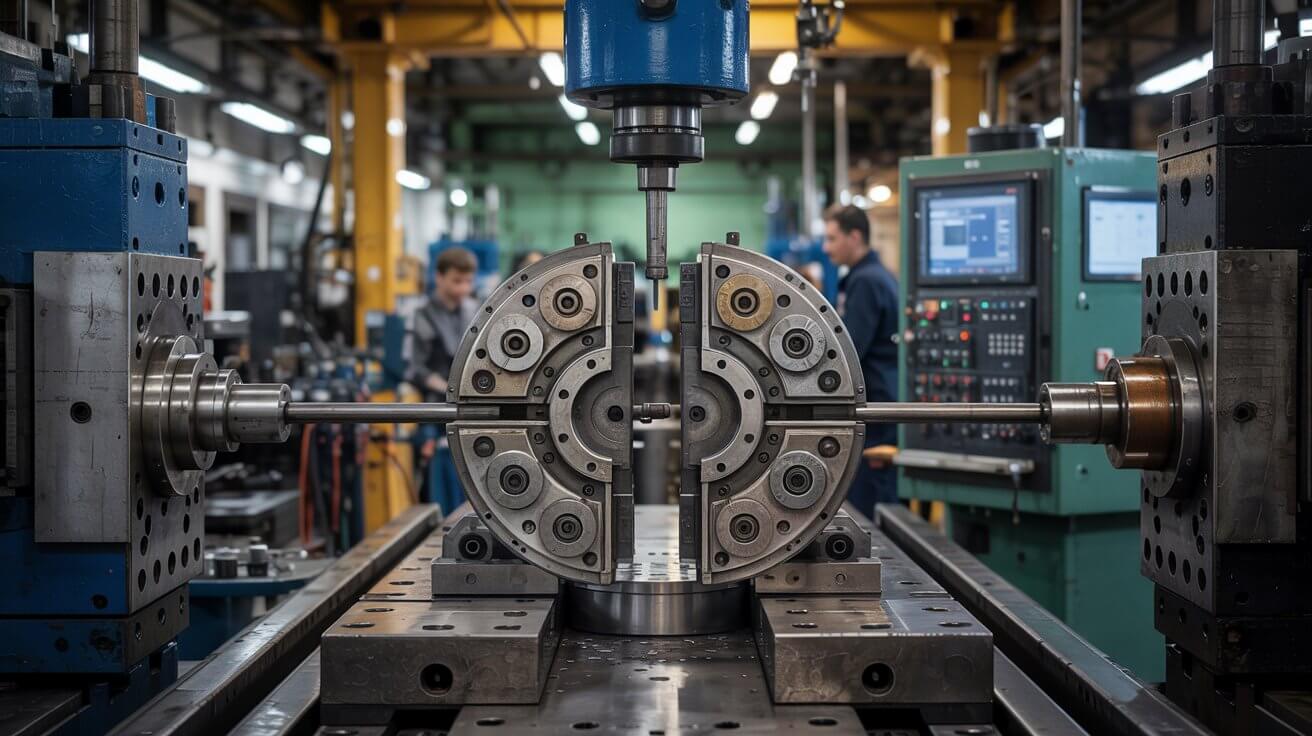
The mold halves are closed and clamped securely together. This creates a cavity in the shape of the desired part.
Read More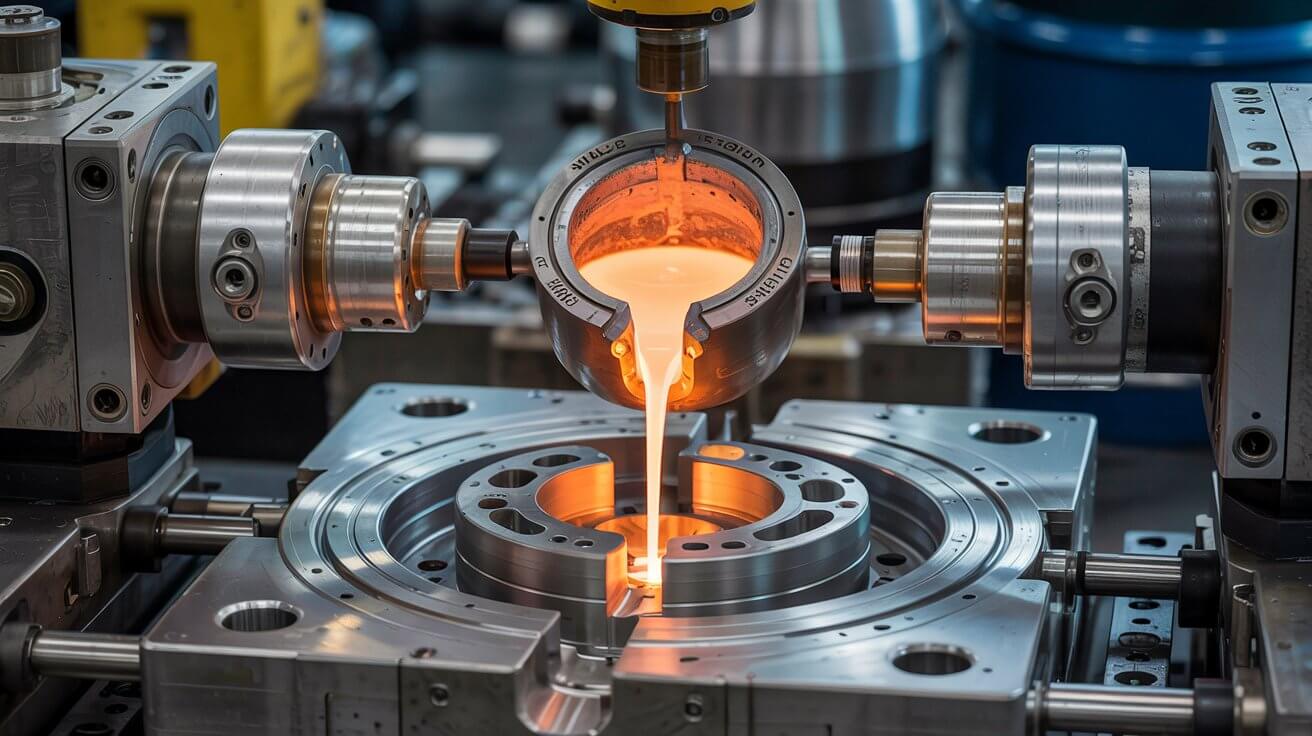
Molten metal, typically aluminum or other non-ferrous alloys, is poured into the mold cavity from a ladle or a furnace. The metal fills the cavity under the force of gravity.
Read More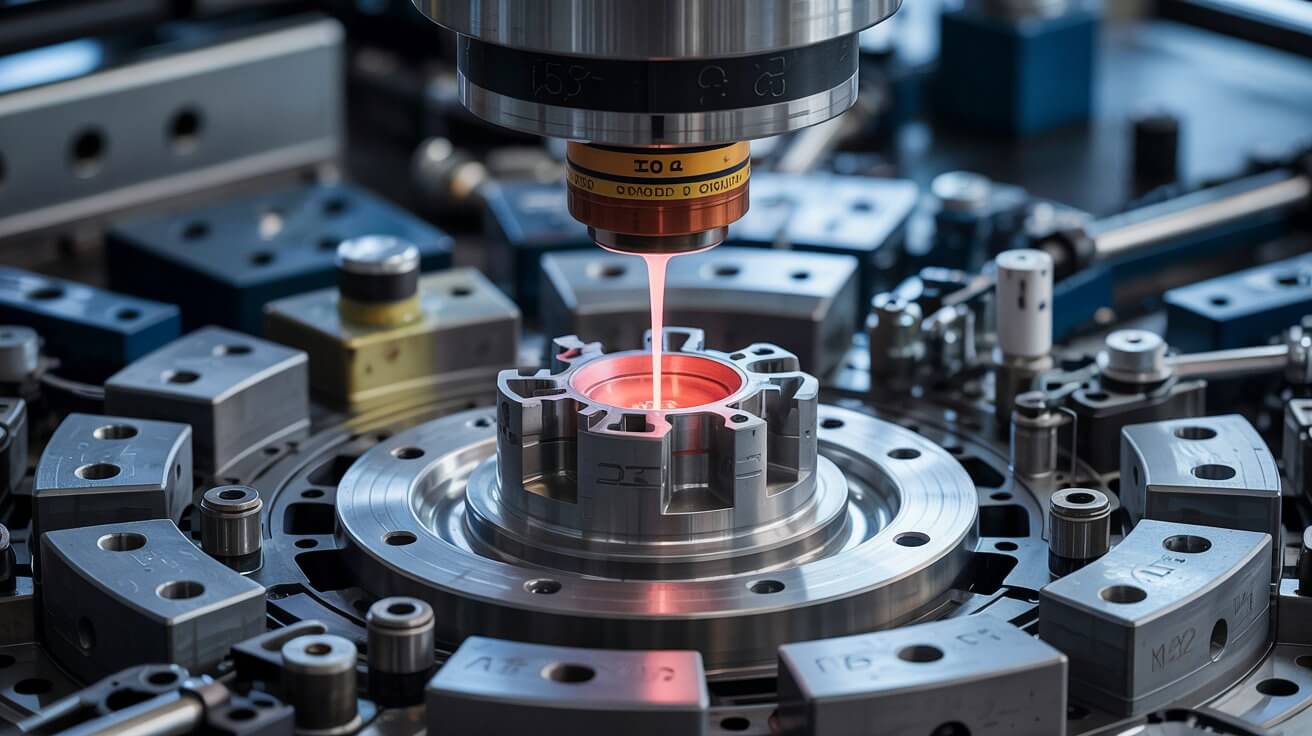
Once the cavity is filled, the molten metal starts to solidify. The cooling rate is controlled to ensure proper solidification without defects.
Read More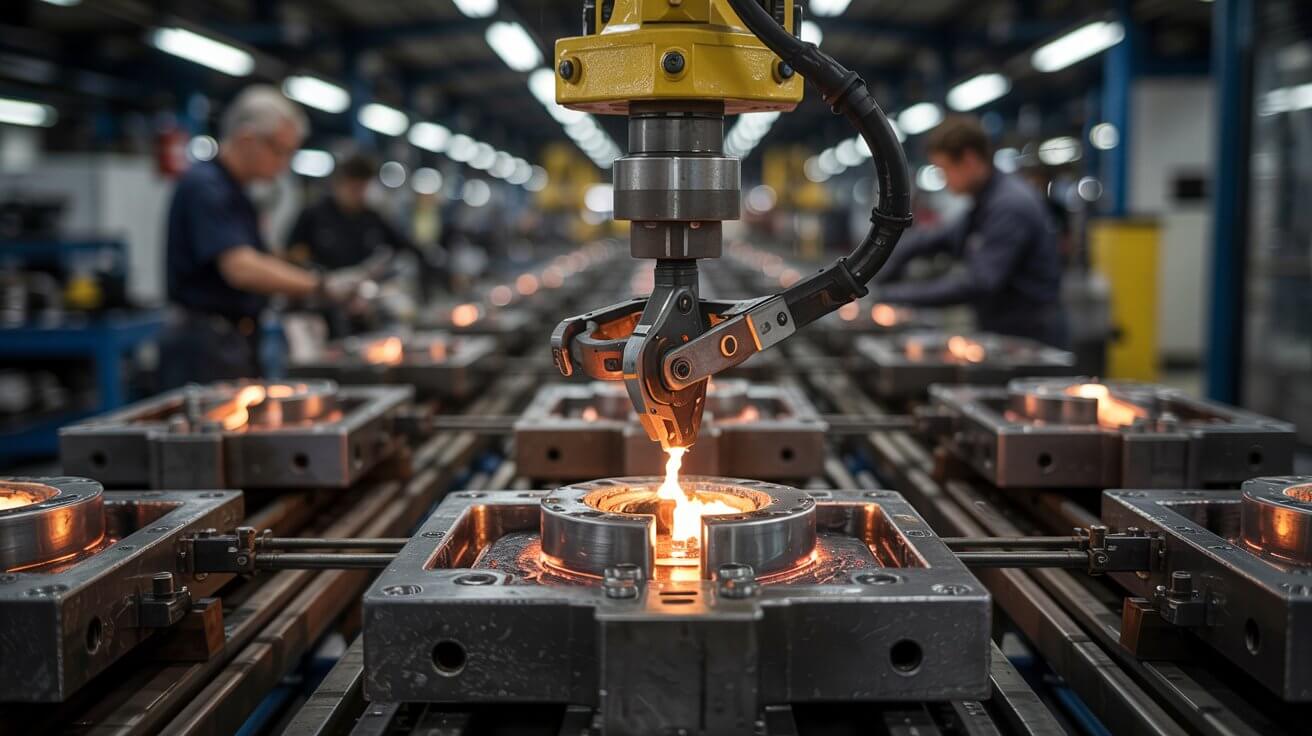
After the metal has solidified, the mold is opened, and the casting is removed. The casting may require further finishing operations such as trimming excess material, machining, or surface treatment to meet final specifications.
Read MoreThe advantages of investment casting are impressive. Create almost any configuration of your precision metal component with High Dimensional Accurcy and Superior surface finishing at very compitative cost. A Design parts as small, large, or complex as you need. In short, eliminate many of the barriers holding you back today.
Consider the following investment casting benefits, which can also help you:
Aluminum Die Casting Alloys are used in a wide range of industries due to their lightweight nature, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance. Common applications include automotive parts, aerospace components, and products in the electrical, industrial, and construction sectors.
By definition, a prototype is the first, preliminary model that allows design engineers the ability to quickly and efficiently explore their designs, test their performance, and craft even better components. After all, production components will be modeled and copied from this initial part.
When the prototype is the building block essential to the success of a project, don’t be forced to choose a prototyping supplier based on time and cost. So much can be learned from a prototype’s function, the need for a quality prototype is critical. When designing metal components, an exact replica of your final part is the best prototype you can get.
Crunch time may mean different things for different projects, but one thing’s for sure, nobody wants unforeseen surprises.
Stopping to prototype your design, evaluate its feasibility, and ensure its productivity might be critical to your product’s ultimate success. But at this stage of a product’s lifecycle, timing is essential. A delay of weeks can result in lower sales and lost market share.
Our in-house rapid prototyping can significantly accelerate your time-to-market. We simulate production using the specific process and our proprietary wax to deliver the most accurate results at a fraction of the time it takes other investment casting companies.
When it comes to developing your ideas, we’ve got the most effective prototyping options for your component—not to mention the in-house prototyping experts to help you choose the right one for the job. Our prototyping capabilities include:
Rajhans does not have a minimum order quantity for prototypes. So whether you need one or one hundred, our team can provide a consistent supply of production-like components.
Best of all, we can create prototypes in as little as five days. Our average tooling lead time is three to five days. Lead times can vary based on complexity of the part and overall project needs.
We know that finding a supplier who can constantly and consistently supply prototypes can make or break your business. Investment cast prototyping is efficient in the overall cost and time of the project. The best thing is, you do not have to compromise quality for time or cost. Our in-house team of knowledgeable engineers are constantly thinking outside of the box to ensure our customer’s designs become a successful reality. Let us help you succeed.
