Surface treatment encompasses a variety of processes designed to alter the surface properties of materials to enhance appearance, performance, and durability. These treatments can improve corrosion resistance, wear resistance, electrical conductivity, and aesthetic appeal, making them vital across various engineering applications.
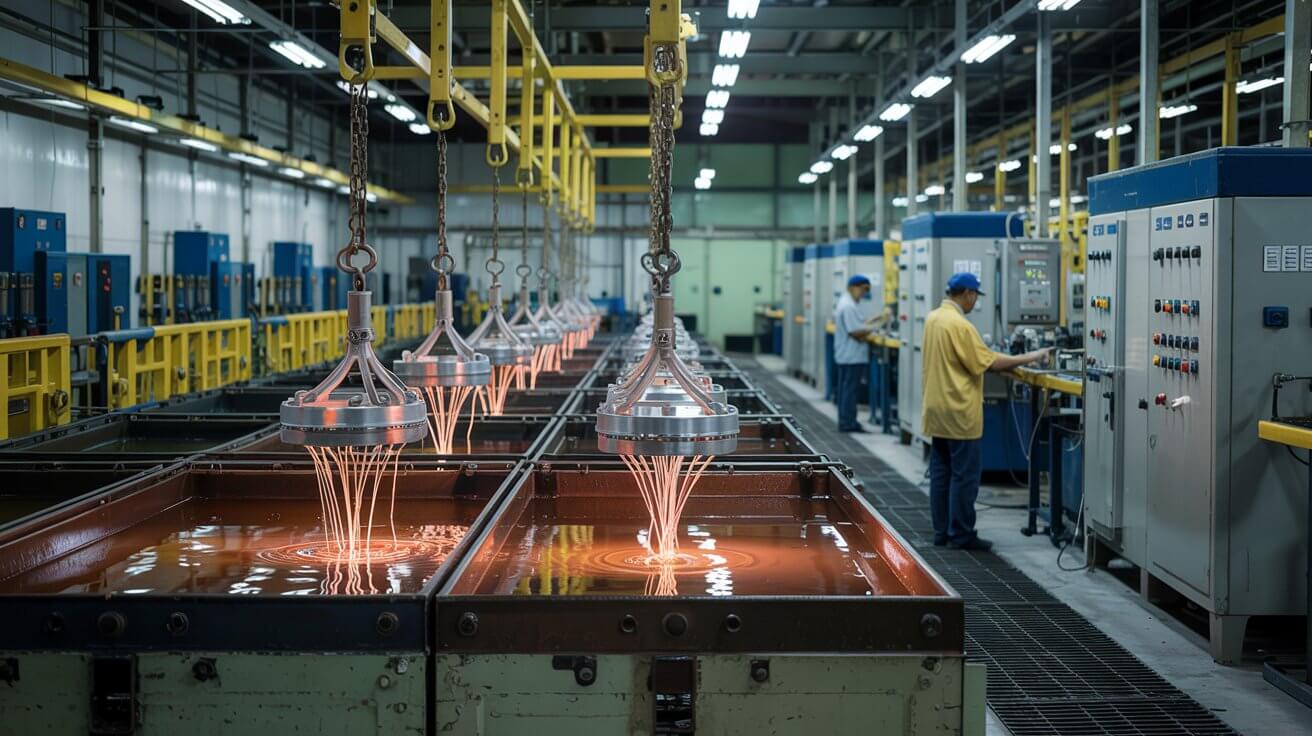

Electroplating: Involves depositing a thin layer of metal onto the surface of a workpiece using an electric current. Common metals used include chrome, nickel, zinc, and gold. Electroless Plating: A chemical process that deposits a metal coating without the use of an electric current. It provides uniform thickness and is used for metals like nickel and copper.
Read More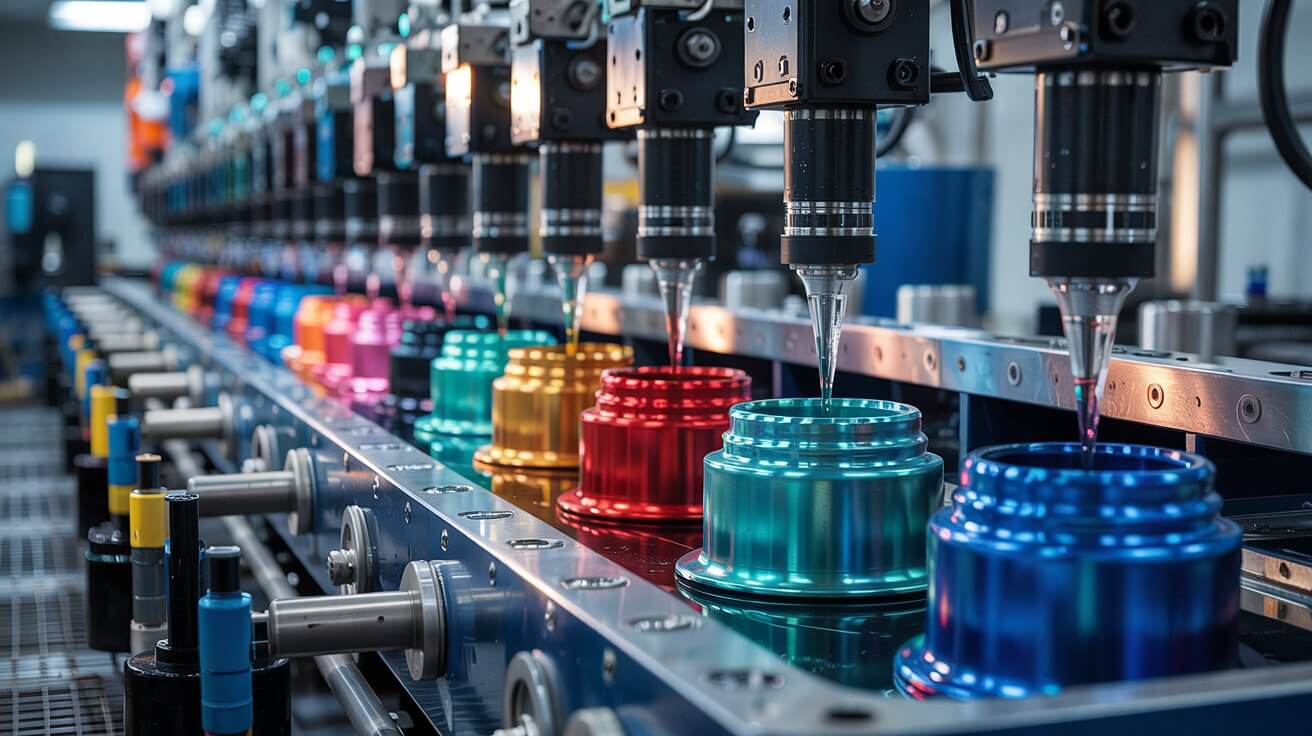
An electrolytic process that forms a protective oxide layer on the surface of aluminum and other metals. This layer enhances corrosion resistance and can be dyed for decorative purposes.
Read More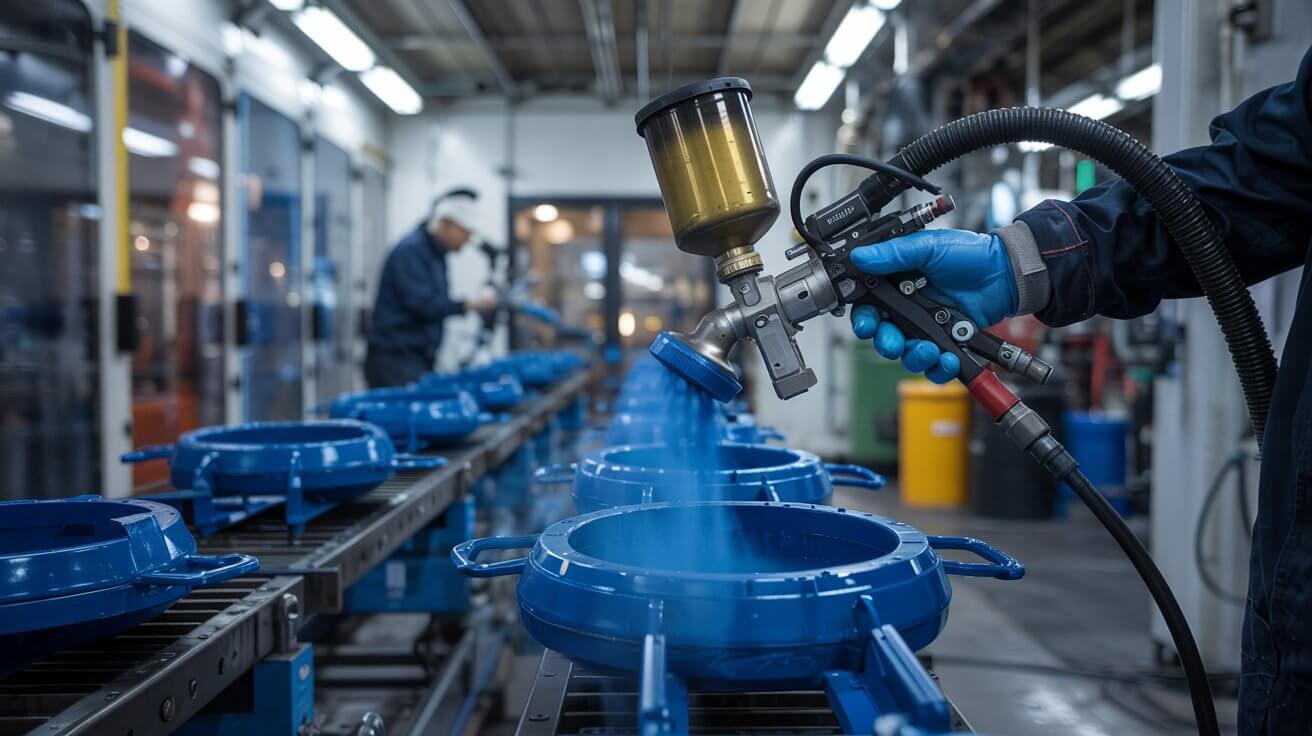
Powder Coating: Involves applying a dry powder to a surface and then curing it under heat to form a hard, durable coating. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Liquid Coating: Traditional paint application that provides a protective and decorative finish.
Read More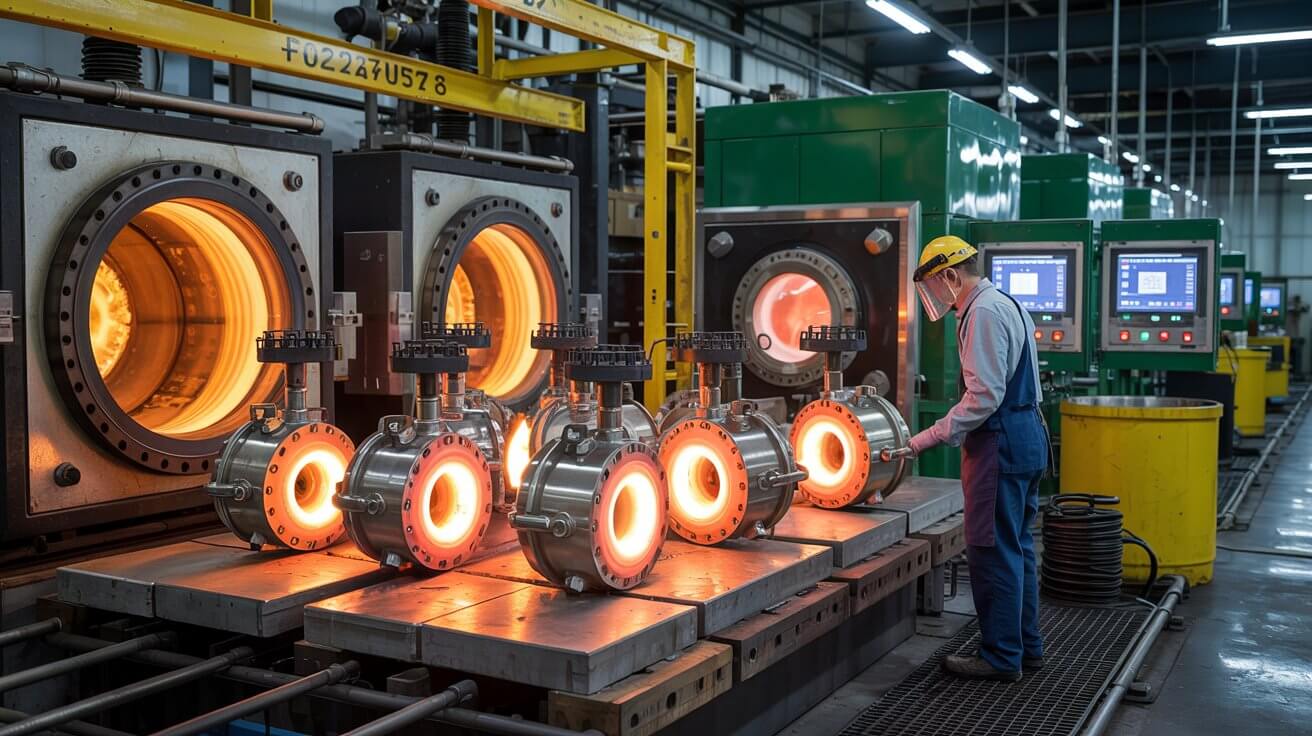
Case Hardening: Involves hardening the surface of a metal workpiece to improve wear resistance while maintaining a softer, ductile core. Methods include carburizing, nitriding, and carbonitriding.
Read More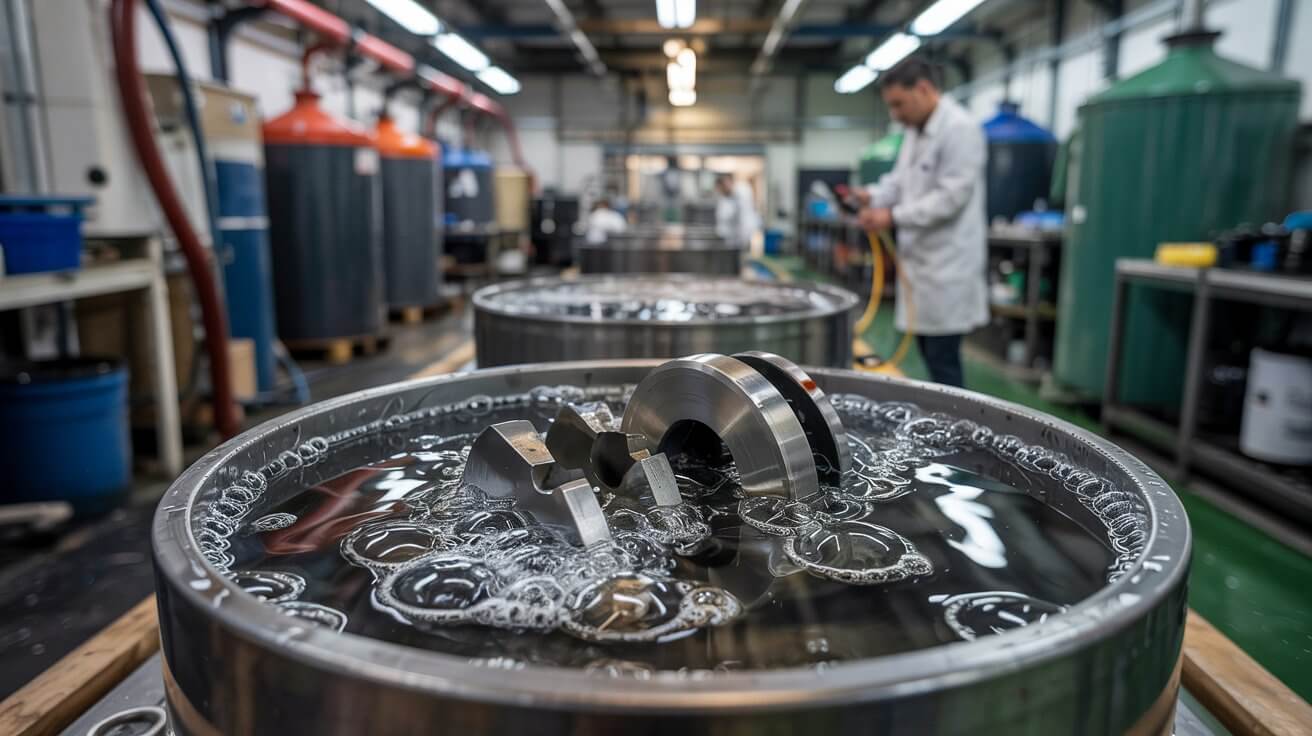
Passivation: Treating stainless steel and other metals with an acid solution to remove contaminants and enhance corrosion resistance. Phosphating: Applying a phosphate coating to steel surfaces to improve corrosion resistance and paint adhesion.
Read More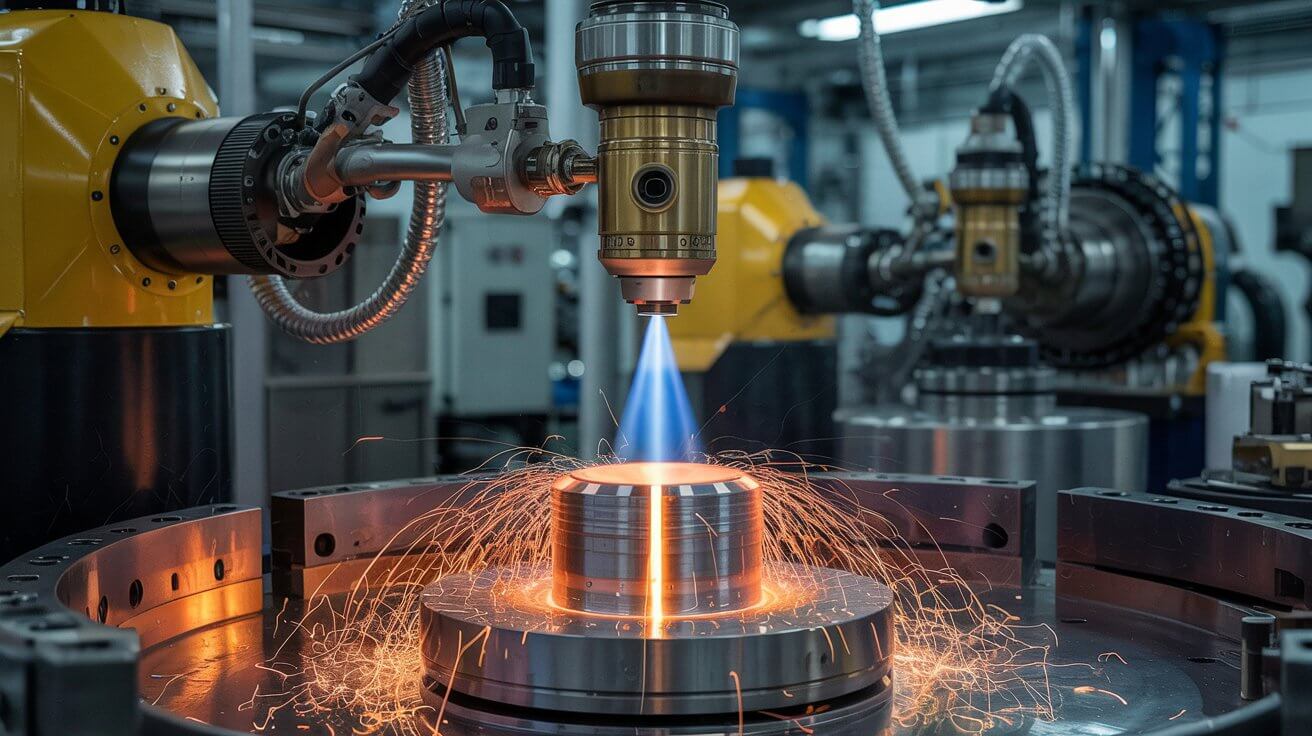
Involves spraying molten or semi-molten materials onto a surface to form a coating. This method can apply metals, ceramics, and polymers to improve wear and corrosion resistance.
Read More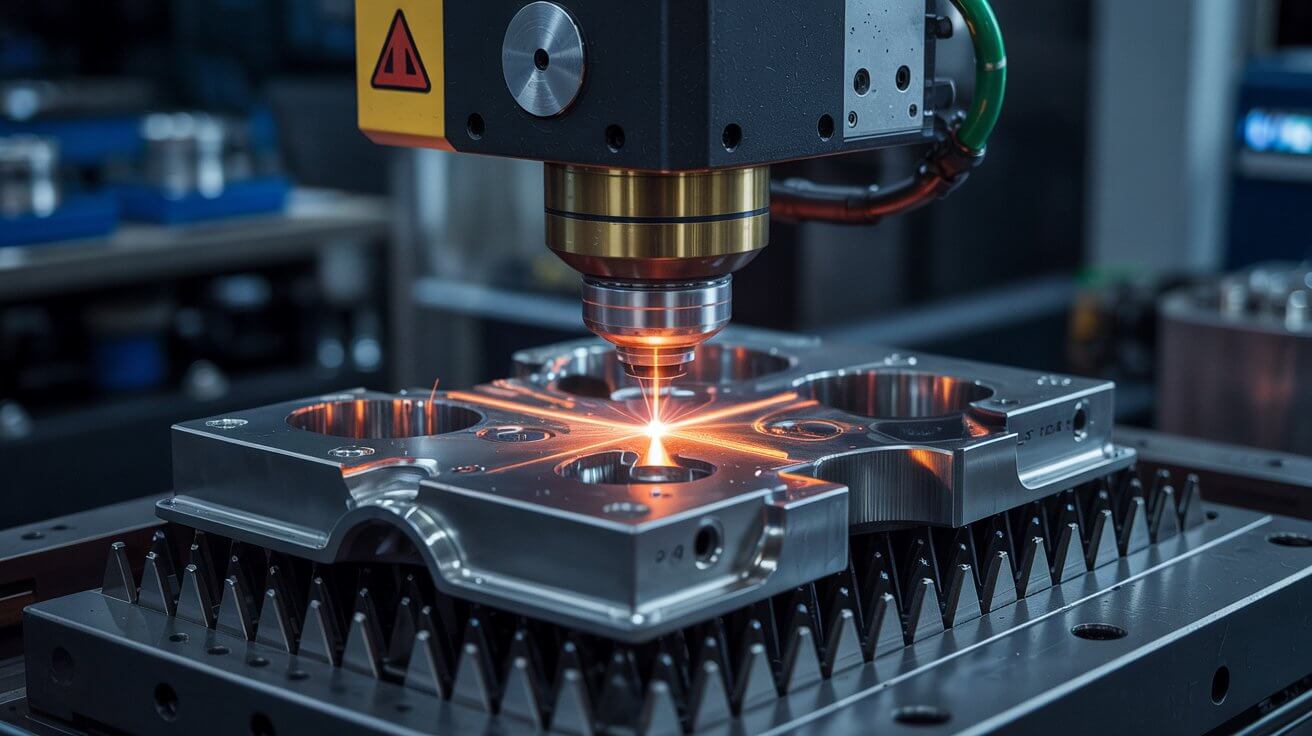
Uses focused laser energy to alter the surface properties of a material. Applications include laser hardening, laser cladding, and laser texturing.
Read More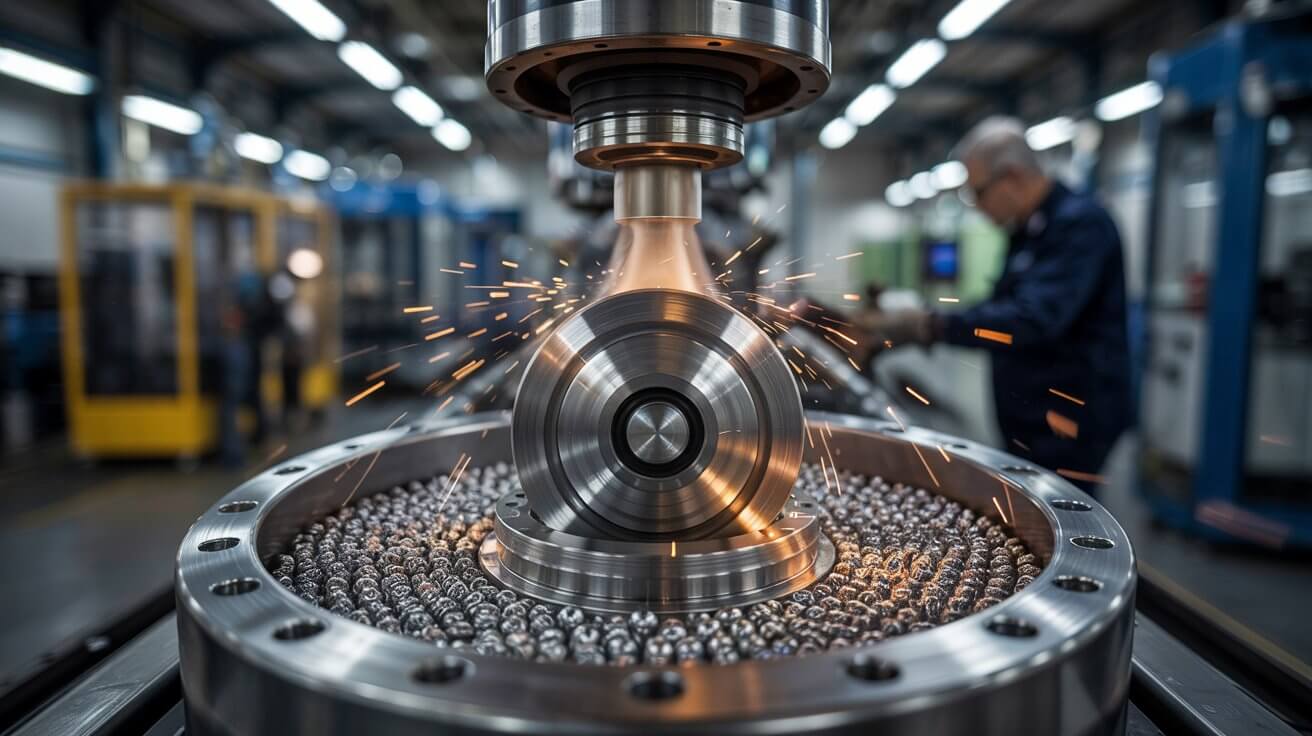
Shot Peening: Bombarding a surface with small spherical media to induce compressive stresses and improve fatigue resistance. Polishing: Using abrasive materials to smooth and enhance the surface finish of a workpiece.
Read More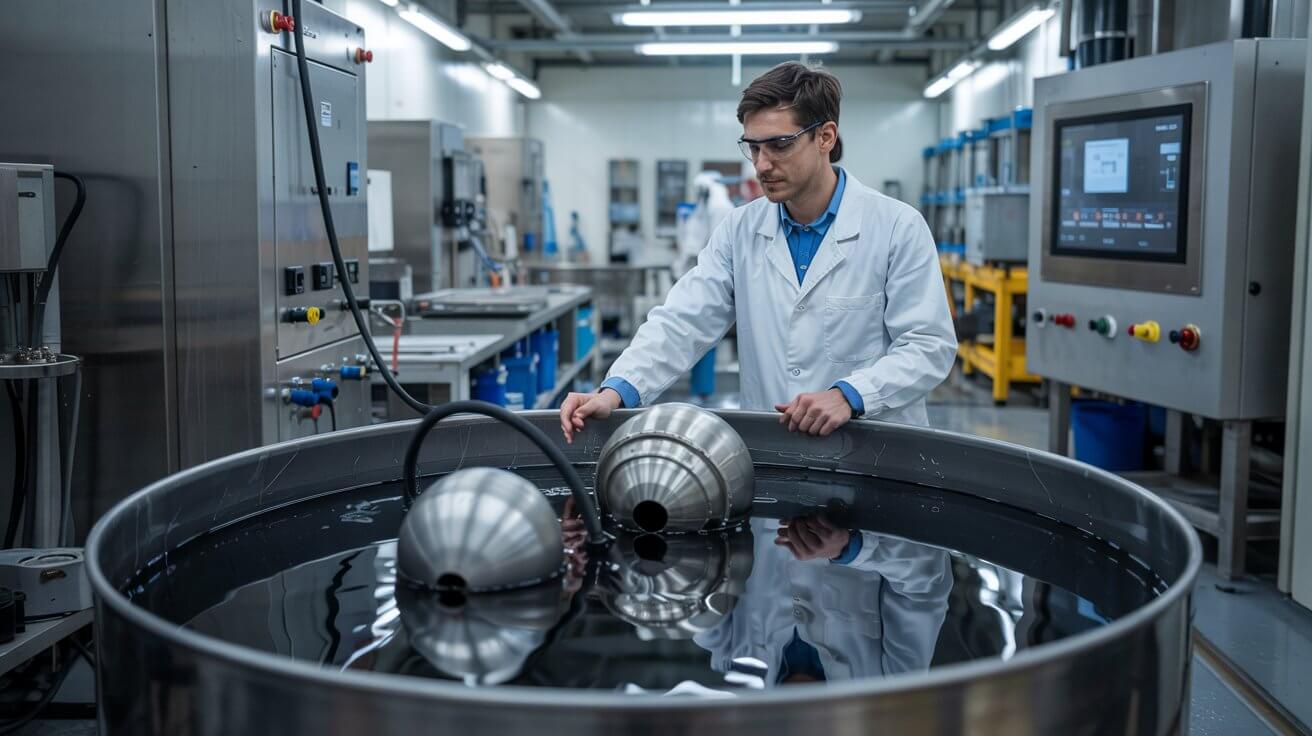
An electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of material from the surface to improve smoothness and shine, often used for stainless steel.
Read MoreMetal surface treatments offer several key benefits, primarily enhancing a metal's durability, functionality, and appearance. These treatments protect against corrosion, wear, and friction, while also improving aesthetics and conductivity. They can also be crucial for preparing a metal surface for further processes like painting or coating.
